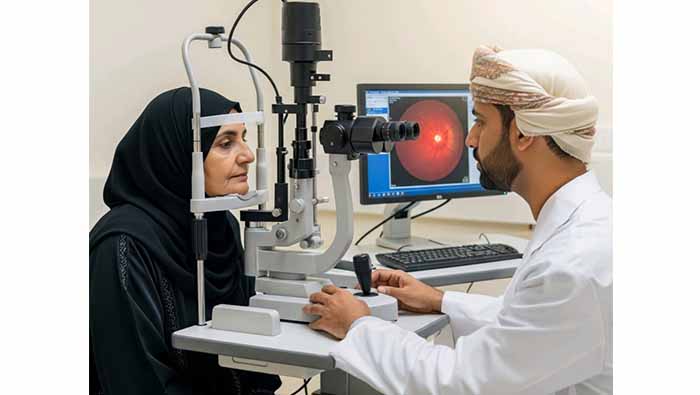
Muscat: The National Programme for Early Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy using artificial intelligence (AI) technologies has successfully screened over 10,000 eligible patients. This achievement reflects the programme's rapid implementation and its impact on preventing retinopathy complications and protecting diabetic patients from the risk of vision loss.
The AI-powered national screening programme has expanded its services to 25 health centres across all governorates of the Sultanate of Oman. This expansion is part of national efforts to enhance ophthalmology services, leverage modern technologies, and utilise AI to support early diagnosis and ensure timely access to screening and treatment.
Dr. Majid Salim Al Shaibani, Retina and Intraocular Inflammation Consultant at Al Nahdha Hospital and Operational Director of the National Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Program, told Oman News Agency (ONA): “Since the programme's nationwide launch, we have screened over 10,000 patients in less than six months, detecting numerous retinopathy cases at early stages before noticeable symptoms appeared."
He added that preliminary data indicates a detection rate exceeding 30% of screened cases—a level of effectiveness unattainable before the introduction of AI technologies.
Dr. Al Shaibani explained that diabetic retinopathy is a silent disease in its early stages, often diagnosed only after serious complications arise. Early detection enables prompt intervention, whether through close monitoring, laser treatment, or intraocular injections, significantly reducing the risk of progression to advanced stages that may cause permanent blindness. This aligns with global recommendations to prevent diabetes-related blindness.
Regarding referral mechanisms, he noted that the programme is electronically linked to the national health records system (Shifa), allowing detected cases requiring further evaluation or treatment to be directly referred to specialised eye clinics in reference hospitals. Priority is determined based on severity to ensure urgent cases receive timely care.
He pointed out that the program utilizes globally approved AI systems for retinal image analysis, capable of detecting various stages of diabetic retinopathy. These advanced deep-learning algorithms provide results within seconds of image capture. The AI models were trained on hundreds of thousands of high-quality global images and validated across diverse populations, with local verification conducted at Oman's dedicated reading center to ensure clinical accuracy.
Dr. Al Shaibani highlighted plans to develop a localised AI database incorporating demographic and epidemiological characteristics to improve diagnostic precision. The program also coordinates with periodic diabetes check-ups, integrating retinopathy screening with other essential tests (e.g., diabetic foot exams, kidney function, blood pressure) into a single visit for patient convenience.
He underlined awareness campaigns targeting diabetic patients through clinic staff, electronic reminders, social media, and educational materials to stress the dangers of delayed screening. Parallel community outreach initiatives aim to increase participation and encourage pre-symptomatic testing.
As the third country globally to implement such an AI-driven initiative, Oman demonstrates its commitment to adopting cutting-edge technologies for enhanced diagnostic accuracy, cost efficiency, and timely intervention. The programme covers all Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes patients, playing a pivotal role in preventing vision loss through early detection.